Call & Put Options
If you would like to learn more, you are encouraged to complete the Premia Academy Options 101 courses, which can be found at https://academy.premia.blue/
Options Primer
Call (put) options are financial derivatives that give their buyer the right to buy (sell) an underlying token at a specified strike price and expiration date. For example, a call option could give you the right to buy 1 ETH at a price of $2,000 next Sunday.
Options are the most popular financial product to express views on volatility (and directional exposure). They exhibit traits that allow users to curate their desired risk profiles by combining multiple options or using various expirations/strikes as part of a strategy.
Another popular use case for options is hedging (i.e. buying insurance against). Put options are commonly used to hedge the downside risk of one's spot position, while call options can be used to hedge the upside risk of tokens one doesn't have exposure to.
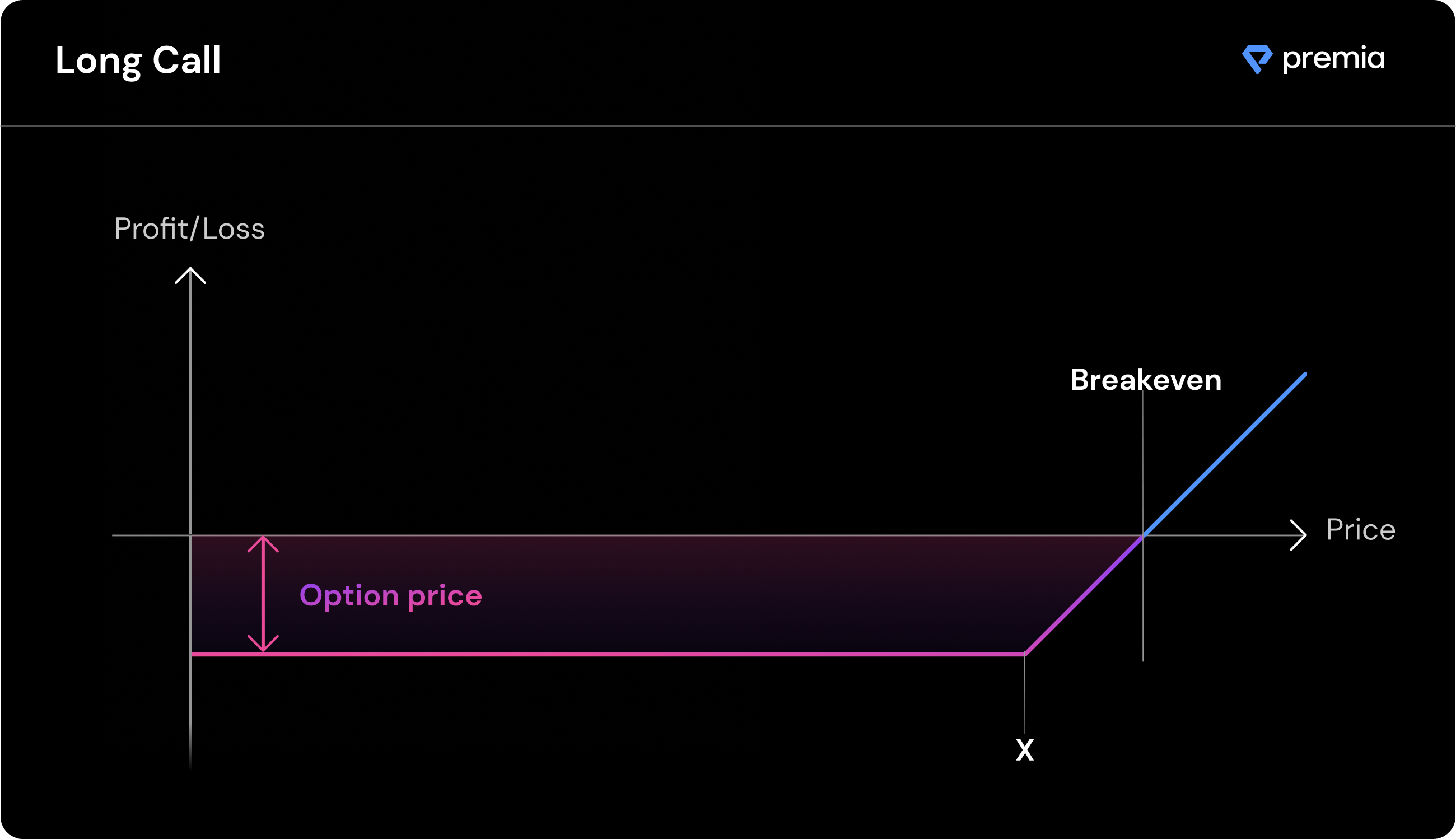
Call Options
Call options provide their holder the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the described amount of underlying tokens at the specified strike price and expiration date.
Buyers of call options believe the underlying token could go up in price over time beyond the cost of the premium paid.
Example: John believes that the price of ETH, which is currently trading at $3,000, will increase in the near future.
John decides to purchase a call option on ETH with a strike price of $3,200, expiring in three months. The premium (cost) of the option is $150. Three months later, the price of ETH has indeed increased, and its now trading at $3,500. The option can be exercised (used) to make a profit.
Profit = marketprice - (strikeprice + premium)
In this example, John successfully profited from a long call position.
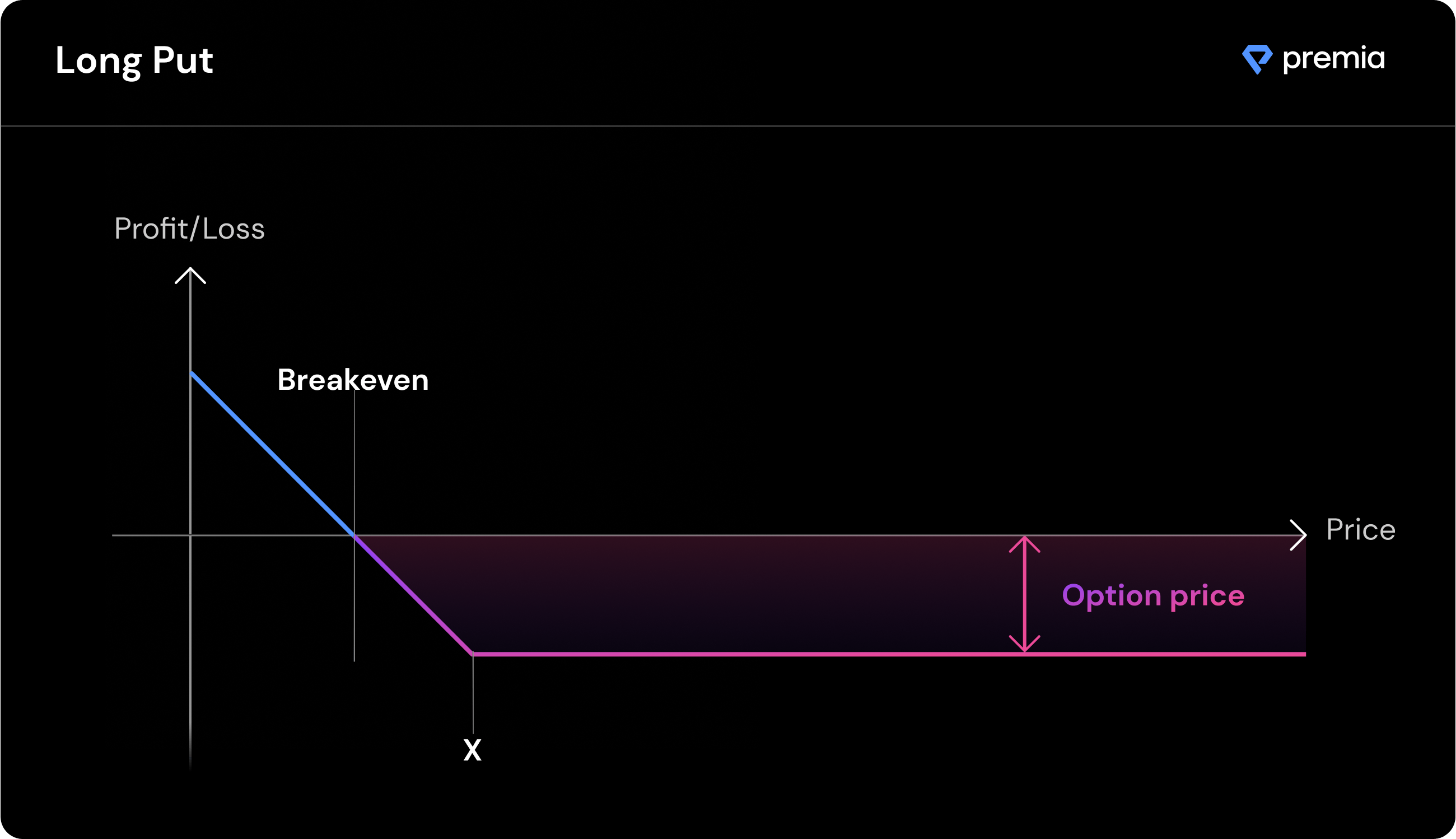
Put Options
Put options provide their holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell the described amount of underlying tokens at the specified strike price and expiration date.
Buyers of put options believe the underlying token could go down in price over time beyond the cost of the premium paid.
John holds ETH and is anticipating prices to fall on the long term. He purchases a put option on ETH with a strike price of $2,800 and an expiration date in three months. The premium of the option is $200. Three months later, ETH is now trading at $2,500. The put option can be exercised for a profit, offsetting the losses of the ETH spot position.
In this example, John successfully hedged his existing spot position with a long put, offsetting some of his losses.
Profit = strikeprice - (marketprice + premium)
Next
Options on Premia